Medical Ultrasound Imaging
Wednesday, 2 April 2025
'Mode' p20 Searchterm 'Mode' found in 134 articles 14 terms [ • ] - 120 definitions [• ] Result Pages : •  From Fukuda Denshi Co., Ltd.;
From Fukuda Denshi Co., Ltd.;'Multi-Purpose Portable Scanner Multi-Frequency Function enables selection of 3 frequencies in each Transducer High-End image Control Function as Zoom, Image Processing, and Variable Focal Zones Built-in Large Track Ball allows ease of use B, B/B, M, and B/M-mode display General Calculation Package for OB, Distance, Area, Volume, and Cardiovascular OB Calculation shown on report page Wide Band, High sensitivity New optional probes' • 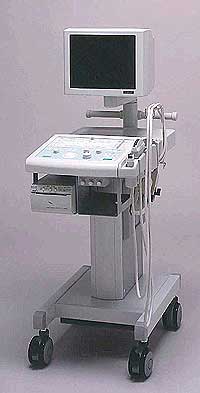 From Fukuda Denshi Co., Ltd.;
From Fukuda Denshi Co., Ltd.;'Operation-friendly Switches and Controls backlit to permit the operator to identify them in a darkroom Image Optimization through Ultrasonic Frequency Changeover without replacement of the probe High frame rate enhancement mode for Cardiac echo Cine memory for selection of best data through SCROLL, LOOP, or MANUAL review Programmable function keys allow to get predefined for measurement parameters. Special measurement software usable in a wide range. Measurement Report page on the display can be printed as required.' •
Fetal ultrasound is a safe and non-invasive imaging technique used to visualize and monitor the development of a fetus during pregnancy. It employs high-frequency sound waves to create detailed images of the baby, the placenta, and the uterus. Fetal ultrasound provides valuable information about the baby's growth, organ development, and overall well-being. It is commonly used to determine gestational age, assess fetal anatomy, detect abnormalities, and monitor fetal movements and heart rate. This essential tool enables healthcare professionals to ensure the optimal health of both the mother and the baby throughout the pregnancy. The FDA (Food and Drug Administration) has established regulations governing ultrasound usage, including specific guidelines for fetal ultrasound examinations. These regulations permit an eight-fold increase in ultrasound intensity for fetal scans. They place considerably responsibility on the user to understand the output measurements, the mechanical index (MI), the thermal index (TI) and to use them in their scanning. The primary safety concern in prenatal diagnostic imaging is temperature rise. It is known that hyperthermia is teratogenic. The efforts of investigators have concentrated on defining the temperature increases and exposure times which may give rise to biological effects and on determining the ultrasound levels which might, in turn, lead to those temperature rises. In fetal ultrasound, the highest temperature increase would be expected to occur at bone and the thermal index with bone at/near the focus (TIB) would give the 'worst case' conditions. The mechanical index and thermal index must be displayed if the ultrasound system is capable of exceeding an index of 1. The displayed indices are based on the manufacturer's experimental and modeled data. However, an independent study has demonstrated significant discrepancies over declared spatial peak time averaged intensity (I-SPTA) output of up to 400%. See also ALARA Principle, Pregnancy Ultrasound and Doppler Fluximetry in Pregnancy. Further Reading: Basics:
•
Frame averaging is a form of lowpass filtering. With frame averaging temporal variation are smoothed by addition of consecutive frames in a real-time mode.
•
Fundamental imaging describes ultrasound imaging and Doppler modes in which the received signal is acquired and processed under the assumption of linear propagation and scattering. See also Contrast Pulse Sequencing. Result Pages : |
Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging.com
former US-TIP.com
Member of SoftWays' Medical Imaging Group - MR-TIP • Radiology TIP • Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging
Copyright © 2008 - 2025 SoftWays. All rights reserved.
Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Advertise With Us
former US-TIP.com
Member of SoftWays' Medical Imaging Group - MR-TIP • Radiology TIP • Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging
Copyright © 2008 - 2025 SoftWays. All rights reserved.
Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Advertise With Us
[last update: 2023-11-06 01:42:00]




