Medical Ultrasound Imaging
Wednesday, 2 April 2025
'Medical Imaging' p5 Searchterm 'Medical Imaging' found in 41 articles 4 terms [ • ] - 37 definitions [• ] Result Pages : • •  From CHISON MEDICAL IMAGING CO., LTD.;
From CHISON MEDICAL IMAGING CO., LTD.;Vet scanner for abdominal, reproduction, small parts, urology, cardiology, and tendon of dogs, cats, equine etc. • 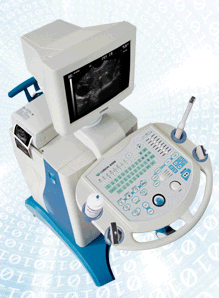 From CHISON MEDICAL IMAGING CO., LTD.;
From CHISON MEDICAL IMAGING CO., LTD.;Convex and linear scanner for abdominal, Obs/Gyn, small parts, urology, cardiology, proctology and pediatrics. • 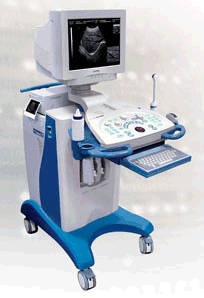 From CHISON MEDICAL IMAGING CO., LTD.;
From CHISON MEDICAL IMAGING CO., LTD.;PC-based scanner for abdominal, Obs/Gyn, small parts, urology, cardiology, proctology, pediatrics with four 4-step multi-frequency probes. •
Doppler ultrasound is a medical imaging technique for calculating the relative velocity between two points by measuring the frequency shift of a sound wave transmitted from one point to the other, based on the Doppler effect. Continuous or pulsed Doppler is frequently used to examine cardiovascular blood flow. The combination of routine 2D-mode and Doppler ultrasound allows a complete evaluation of the heart's anatomy and function (including the fetal heart). See also Doppler Fluximetry in Pregnancy. Doppler ultrasound depends on the fact that if a moving object reflects the ultrasound waves, the echo frequencies are changed. A higher frequency is created if the object is moving toward the probe//transducer and a lower frequency if it is moving away from it. How much the frequency is changed depends upon how fast the object is moving. Doppler ultrasound shows the different rates of blood flow in different colors on a monitor in real time. The major Doppler parameters are the peak systolic velocity and the end-diastolic velocity. The peak systolic velocity ratio compensates the variability between different patients and instrumentations. Different Doppler and duplex techniques: Further Reading: News & More:
Result Pages : |
Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging.com
former US-TIP.com
Member of SoftWays' Medical Imaging Group - MR-TIP • Radiology TIP • Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging
Copyright © 2008 - 2025 SoftWays. All rights reserved.
Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Advertise With Us
former US-TIP.com
Member of SoftWays' Medical Imaging Group - MR-TIP • Radiology TIP • Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging
Copyright © 2008 - 2025 SoftWays. All rights reserved.
Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Advertise With Us
[last update: 2023-11-06 01:42:00]





 From
From